Middle ear infection or acute otitis media is an infection located behind the eardrum. This type of ear infection usually comes on with a cough or cold and is the commonest type of ear infection in children. While middle-ear infections are prevalent among children, they can also affect adults. An ear infection in an adult could suggest a more severe issue compared to a child, potentially requiring further diagnostic procedures.
External ear infection or Otiits externa is an infection of the ear canal. It is the most common type of ear infection in adults. It is usually caused by water pushing bacteria down the ear canal. Some patients may have structural problems with the ear which can make them prone to this type of infection. Some structural problems can be corrected.
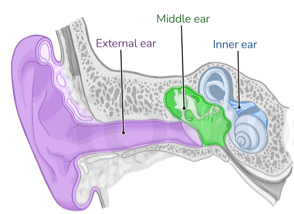
This type of infection is common in children. It usually starts with a cough or cold. The infection tracks up the eustachian tube to the middle ear cavity. Pressure caused by the infection results in stretching of the ear drum which leads to severe pain. After a day or two the ear drum perforates which allows the infection out. This relieves the pain and causes the new symptom of ear discharge. In 99% of cases the ear drum heals after a week or so. Long term complications are very rare even when the infection re-occurs often. Most of these infections require no treatment except calpol to help with the pain. These infections can happen often in some children. It can be a distressing situation for both the child and parent. There are several treatments we can try in this situation, each with their advantages and disadvantages. These include vaccination, long term antibiotics and grommets. Children normally grow out of this situation around the age of 8.
Traditional middle ear infections as detailed above describes how the infection reaches the middle ear from the nose via the eustachian tube. Some patients are walking around with a hole in their ear drum from a previous event which failed to heal properly. The ear drum is not only important for hearing but also as a barrier to infection. Bacteria naturally living in the outer ear can be washed into the middle ear through the perforation and cause an infection that way. It is easily stopped by either keeping the ear out of water or by a straightforward operation to repair the ear drum (myringoplasty).
Typically caused by swimming in dirty water this type of ear infection is very common in adults. It is extremely painful and can have a smelly discharge associated with it. The infection gets in from the outside but is limited to the external ear by the ear drum which protects the middle ear when it is not perforated (99% of people). Some patients are more prone to this type of infection if they have skin conditions like eczema or have structural abnormalities in the ear canal or ear drum such as exostosis, ear drum retractions or more seriously Cholesteatoma (see separate section). It is straightforward to advise you about your ear anatomy during the consultation with the examination microscope.
Rarely an outer ear infection can be caused by fungus. This is otherwise known as thrush or otomycosis. It usually occurs after antibiotic use or in patients with weakened immune systems. It is a bit more stubbon than a bacterial infection usually nad requires several visits to the clinic for removal of the ear canal debris with the use of anti-fungal ear drops in between. Typically the symptoms are itch and blocked ears.
You are more likely to get an ear infection if you:
Smoke or are around someone who smokes
Have a cold or other upper respiratory infection
Have a structural abnormality inside the ear
Have a skin condition like eczema or sensitive skin.

© Copyright 2025 | Jones ENT Surgery | All Rights Reserved